Austria: Emerging Business Opportunities
Market overivew
Austria is an advanced and competitive market, one of the richest countries in the European Union (EU) in terms of GDP per capita. Its multifaceted economic ecosystem encompasses many key industrial sectors, including life sciences, industrial manufacturing, electrics and electronics, food and drink, mechanical and steel engineering, chemicals, the automotive industry and wood processing.
After the Covid-19 pandemic, Austria suffered one of its most prolonged periods of economic downturn since 1945. According to the IMF, the Austrian economy contracted by 1.0% in 2023 and experienced a similar decline in 2024. However, Austrian economic output is predicted to stabilise in 2025 and grow in 2026. The recent economic challenges in neighbouring Germany, Austria’s largest trading partner, have been a significant contributory factor to the recent economic slowdown in Austria, affecting many of the country’s economic sectors.
Austria’s high level of government deficit means that fiscal consolidation is needed to bring the debt‑to‑GDP ratio down. This consolidation involves a mix of tax reforms, spending cuts, efficiency improvements and long‑term fiscal reforms, a strategy which is designed to preserve growth and social cohesion while restoring fiscal sustainability and market confidence.
Foreign business and investment
Despite its small size, Austria is a lucrative market for international businesses, as is evident from the fact that it hosts over 400 international corporate headquarters[1]. The greatest number of international headquarters based in Austria are from the manufacturing sector, followed by the wholesale and retail sectors.
The amount of inward FDI stock in Austria grew slowly and steadily between 2014 and 2024, from around €145.7bn (HK$1.328tn) to over €210.6bn[2] ‑ a compound annual growth rate of 3.8%.
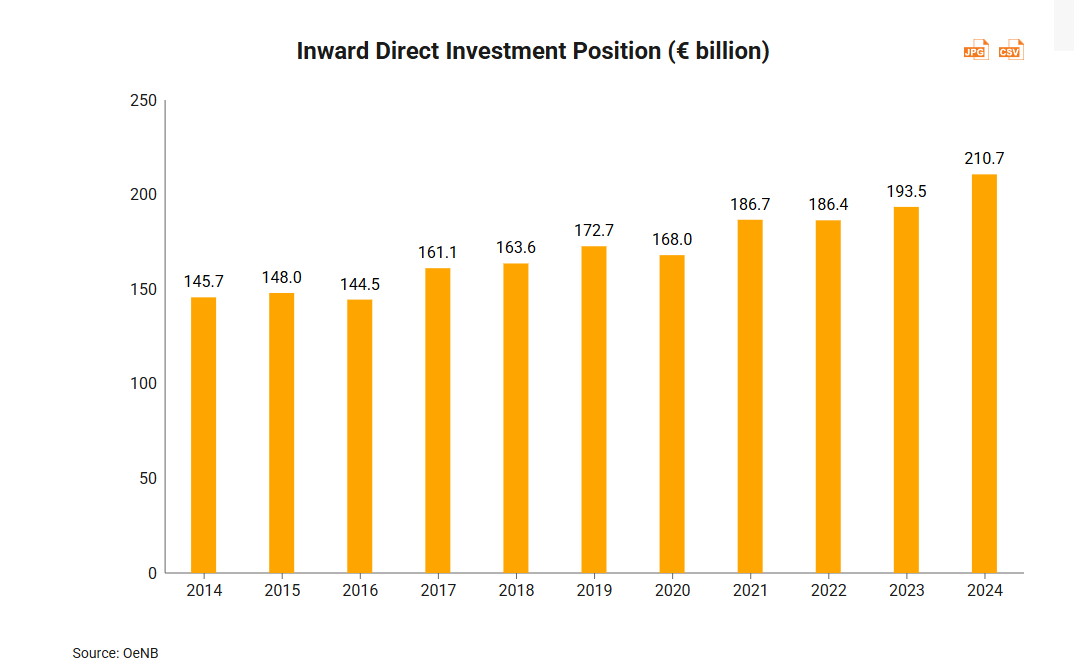
As of 2024, EU countries accounted for almost half of Austria’s FDI. Germany was the largest investor in Austria, accounting for 29% of Austria’s total FDI stock in 2024 and more than half of FDI position from the EU to Austria. After Germany, Russia, Switzerland, the US and Italy were the countries which invested the most in Austria.
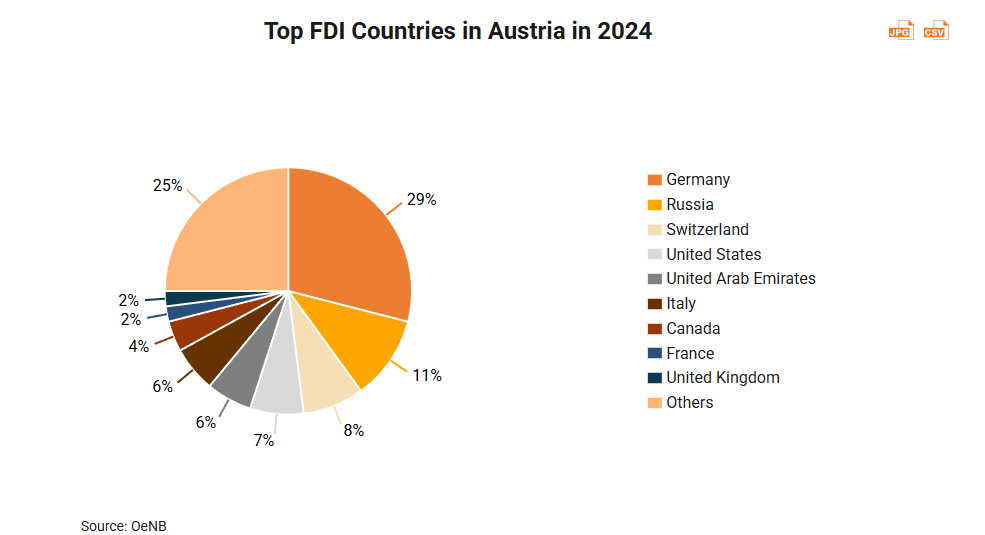
Asia’s FDI position in Austria is relatively small compared to those of Europe and the US, accounting for slightly more than 10% of Austrian inward FDI position in 2024. Among the East Asian economies investing in Austria, Hong Kong ranked second, behind only Japan, with FDI stock valued at €3.2bn.
Over half of inward FDI position was invested in professional, scientific and technical service activities. The next most popular sectors for inward FDI were finance intermediation, trade and real estate.
Innovation in focus
Austria has a strong record when it comes to innovation, ranking eighth highest among the EU member states in the European Innovation Scoreboard 2025. The scoreboard lists Austria as top in the EU in the field of intellectual assets, with the country demonstrating particular strength in patent, trademark and design applications. It also performs well in categories such as linkages, finance and support, firm investment and the attractiveness of research systems. Its high ranking in linkages, in particular, reflects the country’s relative strengths in public‑private co‑publications and collaboration between innovative small‑ and medium‑sized businesses.
Austria also does well when it comes to research and development (R&D) expenditure, ranking second in the EU for its public sector, third for its business sector, and fourth in government support for business R&D. These rankings reflect the robust backing for R&D activities from both the private and public sectors. They also illustrate how Austrian funding bodies and programmes – such as the Austria Research Promotion Agency (FFG) and Austria Wirschaftsservice (aws) – effectively channel essential funding and support to innovative companies.
Austria also performs strongly in the field of eco‑innovation, ranking third in the EU’s Eco-Innovation Index 2024. It is particularly strong when it comes to socio‑economic outcomes, which suggests the country is well able to translate eco‑innovation into positive societal and economic outcomes.
Austria’s vibrant research and innovation landscape is underpinned by robust collaboration between academia, industry and government. This helps to ensure that advanced research is effectively translated into practical applications. This supportive environment has resulted in Austria having one of the highest ratios of R&D expenditure‑to‑GDP in the EU. For a more detailed overview of Austria’s research and innovation ecosystem, please see Austria: An Evolving Research and Innovative Technology Force.
Vienna as the centre of development
Vienna, Austria's capital and largest city, is home to around two million people and is the nation’s undisputed economic engine. In 2023, it was responsible for roughly 25% of Austria’s GDP – approximately €119bn of a total amount of €473bn. Its main strengths are services, innovation and global connectivity. Being at the heart of Central Europe, the city can offer unrivalled connectivity throughout Europe, with most European capitals reachable within three hours by air. This makes Austria an ideal base for businesses focused on Central and Eastern Europe.
Vienna consistently ranks among the world's most competitive and liveable cities. In the 2025 Global Liveability Index[3], it came second, behind only Zurich, excelling in the areas of safety, healthcare, and green spaces. This exceptional quality of life helps attract skilled workers and investment, driving sustained urban prosperity.
As the capital of Austria, Vienna adopts strategic, city‑led approaches to promote sustainable and inclusive growth which are closely aligned with national objectives. The city is recognised for its leadership in smart‑city initiatives, talent competitiveness, and as a key destination for international meetings. To build resilience and cement its status as a premier business location that creates value and jobs, the city launched Vienna 2030 – Economy and Innovation Strategy in 2019 ‑ a comprehensive framework designed to bolster economic vitality and foster advanced innovation.
The strategy focuses on six areas in which Vienna is looking to achieve international excellence. Each area has its own objectives, flagship projects and initiatives. To achieve these objectives, Vienna has taken action in fields such as education, research, key infrastructure development and improving regulatory frameworks. The six areas are:
- Smart Solutions for the Urban Living Space of the 21st Century
Creating innovative, integrated and sustainable urban solutions to enhance the quality of life in Vienna's neighbourhoods while reducing resource consumption and addressing climate challenges. The aim is to achieve this through a blend of technological, organisational and social innovations developed in collaboration with residents, businesses and local partners. - Health Metropolis Vienna
Establishing Vienna as a global leader in integrated urban health and preventive wellbeing by 2030, by building a proactive, accessible and equitable health ecosystem that combines cutting-edge medical research, active urban design and community-based care. The focus is on reducing health disparities, promoting lifelong wellness through movement-friendly cities, and using digital health innovations to support the physical and mental wellbeing of all the city’s residents. - Digitalisation, Vienna-style
Shaping digital transformation in a human-centred, inclusive and value-driven way, by prioritising social cohesion, data sovereignty, public welfare and high ethical standards over purely profit-driven or surveillance-heavy models. This approach positions Vienna as a leading European example of responsible and trustworthy digitalisation, which enhances quality of life, strengthens democratic values and fosters sustainable economic growth while protecting citizens’ rights and privacy. - Smart Production
Making Vienna a global leader in resource-efficient, sustainable and digitally integrated urban manufacturing by 2030. This involves transforming traditional production processes in a densely populated metropolis into smart, circular and innovative systems that minimise environmental impact while maximising economic value and social benefits. It emphasises integrating production into the urban fabric through technologies like Industry 4.0, AI and the Internet-of-Things, while prioritising local supply chains, waste reduction and collaboration between businesses, research institutions and citizens. - Cultural and Creative Metropolis Vienna
Developing Vienna into the preeminent international hub for cultural innovation and creative industries by 2030, by nurturing artistic excellence, interdisciplinary collaboration and entrepreneurial creativity to drive economic growth, social cohesion and international influence. It focuses on expanding the accessible cultural infrastructure, supporting diverse creative talent, and using Vienna’s heritage as a living catalyst for forward-thinking design, media and cultural production. - City of International Encounters
Strengthening Vienna’s position as a vibrant, open, and influential hub for global dialogue and cooperation. This entails attracting and retaining international organisations, enhancing infrastructure and support for major international conferences, and further establishing Vienna’s reputation as a welcoming, well-connected and impactful world city.
Conclusion
Thanks to its economic stability, innovative spirit and strategically important location in Central Europe, Austria offers compelling opportunities for Hong Kong exporters and investors. With strength in areas like advanced technology and manufacturing, healthcare and sustainability, Vienna’s forward‑looking strategies — such as its focus on smart production, digitalisation and integrated urban health — provides an ideal landscape for collaboration and expansion. Hong Kong companies can take advantage of Vienna’s dynamic ecosystem and robust R&D incentives to access and develop the EU market via building new partnerships, testing innovative solutions and establishing a foothold in high‑growth sectors.
[3] The Economist Intelligence Unit





















































First, please LoginComment After ~